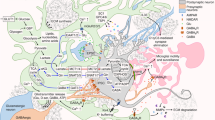
Abstract
In this review we summarize published data on the involvement of glial cells in molecular mechanisms underlying brain plastic reorganization in epilepsy. The role of astrocytes as glial elements in pathological plasticity in epilepsy is discussed. Data on the involvement of aquaporin-4 in epileptogenic plastic changes and on participation of microglia and extracellular matrix in dysregulation of synaptic transmission and plastic remodeling in epileptic brain tissue are reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADAMTS:
-
a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin motifs
- AMPA:
-
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid
- AQP:
-
aquaporins
- AQP4:
-
aquaporin-4 receptor
- BDNF:
-
brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- CSPGs:
-
chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- ECS:
-
extracellular space
- EPSP:
-
excitatory postsynaptic potential
- GABA:
-
gamma-aminobutyric acid
- HAPLN1:
-
hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- LTD:
-
longterm depression
- LTP:
-
long-term potentiation
- mGluRs:
-
metabotropic glutamate receptors
- ММР:
-
matrix metalloproteases
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate
- PDS:
-
paroxysmal depolarization shift
- PNN:
-
perineuronal net
- PV+ :
-
parvalbumin-positive inhibitory interneurons
- SE:
-
status epilepticus
- SIC:
-
slow inward currents
- TLR4:
-
toll-like receptor 4
- tPA:
-
tissue plasminogen activator
References
Ransom, B., Behar, T., and Nedergaard, M. (2003) New roles for astrocytes (stars at last), Trends Neurosci., 26, 520–522.
Halassa, M. M., and Haydon, P. G. (2010) Integrated brain circuits: astrocytic networks modulate neuronal activity and behavior, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 72, 335–355.
De Lanerolle, N. C., and Lee, T. (2005) New facets of the neuropathology and molecular profile of human temporal lobe epilepsy, Epilepsy Behav., 7, 190–203.
Tian, G. F., Azmi, H., Takano, T., Xu, Q., Peng, W., Lin, J., Oberheim, N., Lou, N., Wang, X., Zielke, H. R., Kang, J., and Nedergaard, M. (2005) An astrocytic basis of epilepsy, Nat. Med., 11, 973–981.
Binder, D. K., and Carson, M. J. (2013) Glial cells as primary therapeutic targets for epilepsy, Neurochem. Int., 63, 635–637.
Meldrum, B. S. (1992) Excitatory amino acids in epilepsy and potential novel therapies, Epilepsy Res., 12, 189–196.
Khazipov, R., Valeeva, G., and Khalilov, I. (2015) Depolarizing GABA and developmental epilepsies, CNS Neurosci. Ther., 21, 83–91.
Bonansco, C., and Fuenzalida, M. (2016) Plasticity of hippocampal excitatory-inhibitory balance: missing the synaptic control in the epileptic brain, Neural Plast., 28607038.
Pascual, O., Ben Achour, S., Rostaing, P., Triller, A., and Bessis, A. (2012) Microglia activation triggers astrocytemediated modulation of excitatory neurotransmission, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 109, E197–E205.
Tang, F.-R., and Lee, W.-L. (2001) Expression of the group II and III metabotropic glutamate receptors in the hippocampus of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy, J. Neurocytol., 30, 137–143.
Steinhauser, C., and Seifert, G. (2002) Glial membrane channels and receptors in epilepsy: impact for generation and spread of seizure activity, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 447, 227–237.
Nagaraja, R. Y., Becker, A., Reymann, K. G., and Balschun, D. (2005) Repeated administration of group I mGluR antagonists prevents seizure-induced long-term aberrations in hippocampal synaptic plasticity, Neuropharmacology, 49, Suppl. 1, 179–187.
Carmignoto, G., and Fellin, T. (2006) Glutamate release from astrocytes as a non-synaptic mechanism for neuronal synchronization in the hippocampus, J. Physiol. Paris, 99, 98–102.
Alvarez-Ferradas, C., Morales, J. C., Wellmann, M., Nualart, F., Roncagliolo, M., Fuenzalida, M., and Bonansco, C. (2015) Enhanced astroglial Ca2+ signaling increases excitatory synaptic strength in the epileptic brain, Glia, 63, 1507–1521.
Fellin, T., Gomez-Gonzalo, M., Gobbo, S., Carmignoto, G., and Haydon, P. G. (2006) Astrocytic glutamate is not necessary for the generation of epileptiform neuronal activity in hippocampal slices, J. Neurosci., 26, 9312–9322.
Navarrete, M., and Araque, A. (2008) Endocannabinoids mediate neuron–astrocyte communication, Neuron, 57, 883–893.
Coiret, G., Ster, J., Grewe, B., Wendling, F., Helmchen, F., Gerber, U., and Benquet, P. (2012) Neuron to astrocyte communication via cannabinoid receptors is necessary for sustained epileptiform activity in rat hippocampus, PLoS One, 7, e37320.
Mariotti, L., Losi, G., Sessolo, M., Marcon, I., and Carmignoto, G. (2016) The inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA evokes long-lasting Ca2+ oscillations in cortical astrocytes, Glia, 64, 363–373.
Kogo, N., Dalezios, Y., Capogna, M., Ferraguti, F., Shigemoto, R., and Somogyi, P. (2004) Depression of GABAergic input to identified hippocampal neurons by group III metabotropic glutamate receptors in the rat, Eur. J. Neurosci., 19, 2727–2740.
Somogyi, P., Dalezios, Y., Lujan, R., Roberts, J. D. B., Watanabe, M., and Shigemoto, R. (2003) High level of mGluR7 in the presynaptic active zones of select populations of GABAergic terminals innervating interneurons in the rat hippocampus, Eur. J. Neurosci., 17, 2503–2520.
Lalo, U., Palygin, O., Rasooli-Nejad, S., Andrew, J., Haydon, P. G., and Pankratov, Y. (2014) Exocytosis of ATP from astrocytes modulates phasic and tonic inhibition in the neocortex, PLoS Biol., 12, e1001747.
Ahumada, J., Fernandez de Sevilla, D., Couve, A., Buno, W., and Fuenzalida, M. (2013) Long-term depression of inhibitory synaptic transmission induced by spike-timing dependent plasticity requires coactivation of endocannabinoid and muscarinic receptors, Hippocampus, 23, 1439–1452.
Wetherington, J., Serrano, G., and Dingledine, R. (2008) Astrocytes in the epileptic brain, Neuron, 58, 168–178.
Haglund, M. M., and Hochman, D. W. (2005) Furosemide and mannitol suppression of epileptic activity in the human brain, J. Neurophysiol., 94, 907–918.
Maa, E. H., Kahle, K. T., Walcott, B. P., Spitz, M. C., and Staley, K. J. (2011) Diuretics and epilepsy: will the past and present meet? Epilepsia, 52, 1559–1569.
Feng, Z., and Durand, D. M. (2006) Effects of potassium concentration on firing patterns of low-calcium epileptiform activity in anesthetized rat hippocampus: inducing of persistent spike activity, Epilepsia, 47, 727–736.
Verkman, A. S. (2002) Physiological importance of aquaporin water channels, Ann. Med., 34, 192–200.
Nagelhus, E. A., Mathiisen, T. M., and Ottersen, O. P. (2004) Aquaporin-4 in the central nervous system: cellular and subcellular distribution and coexpression with Kir4.1, Neuroscience, 129, 905–913.
Niermann, H., Amiry-Moghaddam, M., Holthoff, K., Witte, O. W., and Ottersen, O. P. (2001) A novel role of vasopressin in the brain: modulation of activity dependent water flux in the neocortex, J. Neurosci., 21, 3045–3051.
Wolburg, H., Wolburg-Buchholz, K., Fallier-Becker, P., Noell, S., and Mack, A. F. (2011) Structure and functions of aquaporin-4-based orthogonal arrays of particles, Int. Rev. Cell. Mol. Biol., 287, 1–41.
Hsu, M. S., Seldin, M., Lee, D. J., Seifert, G., Steinhauser, C., and Binder, D. K. (2011) Laminar-specific and developmental expression of aquaporin-4 in the mouse hippocampus, Neuroscience, 178, 21–32.
Binder, D. K., Nagelhus, E. A., and Ottersen, O. P. (2012) Aquaporin-4 and epilepsy, Glia, 60, 1203–1214.
Scharfman, H. E., and Binder, D. R. (2013) Aquaporin-4 water channels and synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus, Neurochem. Int., 63, 702–711.
Chin, J., and Scharfman, H. E. (2013) Shared cognitive and behavioral impairments in epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease and potential underlying mechanisms, Epilepsy Behav., 26, 343–351.
Szu, J. I., and Binder, D. K. (2016) The role of astrocytic aquaporin-4 in synaptic plasticity and learning and memory, Front. Integrat. Neurosci., 10, Art.8.
Binder, D. K., Yao, X., Sick, T. J., Verkman, A. S., and Manley, G. T. (2006) Increased seizure duration and slowed potassium kinetics in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels, Glia, 53, 631–636.
Baalman, K., Marin, M. A., Ho, T. S., Godoy, M., Cherian, L., Robertson, C., and Rasband, M. N. (2015) Axon initial segment-associated microglia, J. Neurosci., 35, 2283–2292.
Ahlers, K. E., Karacay, B., Fuller, L., Bonthius, D. J., and Dailey, M. E. (2015) Transient activation of microglia following acute alcohol exposure in developing mouse neocortex is primarily driven by BAX-dependent neurodegeneration, Glia, 63, 1694–1713.
Shigemoto-Mogami, Y., Hoshikawa, K., Goldman, J. E., Sekino, Y., and Sato, K. (2014) Microglia enhance neurogenesis and oligodendrogenesis in the early postnatal subventricular zone, J. Neurosci., 34, 2231–2243.
Arno, B., Grassivaro, F., Rossi, C., Bergamaschi, A., Castiglioni, V., Furlan, R., Greter, M., Favaro, R., Comi, G., Becher, B., Martino, G., and Muzio, L. (2014) Neural progenitor cells orchestrate microglia migration and positioning into the developing cortex, Nat. Commun., 5, 5611.
Sipe, G. O., Lowery, R. L., Tremblay, M. E., Kelly, E. A., Lamantia, C. E., and Majewska, A. K. (2016) Microglial P2Y12 is necessary for synaptic plasticity in mouse visual cortex, Nat. Commun., 7, 10905.
Eyo, U. B., Murugan, M., and Wu, L.-J. (2016) Microglia–neuron communication in epilepsy, Glia, in press, doi: 10.1002/glia.23006.
Boer, K., Spliet, W. G., Van Rijen, P. C., Redeker, S., Troost, D., and Aronica, E. (2006) Evidence of activated microglia in focal cortical dysplasia, J. Neuroimmunol., 173, 188–195.
Avignone, E., Lepleux, M., Angibaud, J., and Nagerl, U. V. (2015) Altered morphological dynamics of activated microglia after induction of status epilepticus, J. Neuroinflamm., 12, 202.
Eyo, U. B., Peng, J., Swiatkowski, P., Mukherjee, A., Bispo, A., and Wu, L. J. (2014) Neuronal hyperactivity recruits microglial processes via neuronal NMDA receptors and microglial P2Y12 receptors after status epilepticus, J. Neurosci., 34, 10528–10540.
Jung, K. H., Chu, K., Lee, S. T., Kim, J. H., Kang, K. M., Song, E. C., Kim, S. J., Park, H. K., Kim, M., Lee, S. K., and Roh, J. K. (2009) Region-specific plasticity in the epileptic rat brain: a hippocampal and extrahippocampal analysis, Epilepsia, 50, 537–549.
Eyo, U. B., Gu, N., De, S., Dong, H., Richardson, J. R., and Wu, L. J. (2015) Modulation of microglial process convergence toward neuronal dendrites by extracellular calcium, J. Neurosci., 35, 2417–2422.
Hickman, S. E., Kingery, N. D., Ohsumi, T. K., Borowsky, M. L., Wang L. C., Means, T. K., and El Khoury, J. (2013) The microglial sensome revealed by direct RNA sequencing, Nat. Neurosci., 16, 1896–1905.
Elmore, M. R., Najafi, A. R., Koike, M. A., Dagher, N. N., Spangenberg, E. E., Rice, R. A., Kitazawa, M., Matusow, B., Nguyen, H., West, B. L., and Green, K. N. (2014) Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor signaling is necessary for microglia viability, unmasking a microglia progenitor cell in the adult brain, Neuron, 82, 380–397.
Ali, I., Chugh, D., and Ekdahl, C. T. (2015) Role of fractalkine-CX3CR1 pathway in seizure-induced microglial activation, neurodegeneration, and neuroblast production in the adult rat brain, Neurobiol. Dis., 74, 194–203.
Banerjee, M., Sasse, V. A., Wang, Y., Maulik, M., and Kar, S. (2015) Increased levels and activity of cathepsins B and D in kainate-induced toxicity, Neuroscience, 284, 360–373.
Lauro, C., Catalano, M., Trettel, F., and Limatola, C. (2015) Fractalkine in the nervous system: neuroprotective or neurotoxic molecule? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1351, 141–148.
Hoshiko, M., Arnoux, I., Avignone, E., Yamamoto, N., and Audinat, E. (2012) Deficiency of the microglial receptor CX3CR1 impairs postnatal functional development of thalamocortical synapses in the barrel cortex, J. Neurosci., 32, 15106–15111.
Paolicelli, R. C., Bolasco, G., Pagani, F., Maggi, L., Scianni, M., Panzanelli, P., Giustetto, M., Ferreira, T. A., Guiducci, E., Dumas, L., Ragozzino, D., and Gross, C. T. (2011) Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development, Science, 333, 1456–1458.
Rogers, J. T., Morganti, J. M., Bachstetter, A. D., Hudson, C. E., Peters, M. M., Grimmig, B. A., Weeber, E. J., Bickford, P. C., and Gemma, C. (2011) CX3CR1 deficiency leads to impairment of hippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity, J. Neurosci., 31, 16241–16250.
Roumier, A., Bechade, C., Poncer, J. C., Smalla, K. H., Tomasello, E., Vivier, E., Gundelfinger, E. D., Triller, A., and Bessis, A. (2004) Impaired synaptic function in the microglial KARAP/DAP12-deficient mouse, J. Neurosci., 24, 11421–11428.
Hayashi, Y., Ishibashi, H., Hashimoto, K., and Nakanishi, H. (2006) Potentiation of the NMDA receptor-mediated responses through the activation of the glycine site by microglia secreting soluble factors, Glia, 53, 660–668.
Rodgers, K. M., Hutchinson, M. R., Northcutt, A., Maier, S. F., Watkins, L. R., and Barth, D. S. (2009) The cortical innate immune response increases local neuronal excitability leading to seizures, Brain, 132, 2478–2486.
Zhang, J., Malik, A., Choi, H. B., Ko, R. W., DissingOlesen, L., and MacVicar, B. A. (2014) Microglial CR3 activation triggers long-term synaptic depression in the hippocampus via NADPH oxidase, Neuron, 82, 195–207.
Li, Y., Du, X. F., Liu, C. S., Wen, Z. L., and Du, J. L. (2012) Reciprocal regulation between resting microglial dynamics and neuronal activity in vivo, Dev. Cell, 23, 1189–1202.
Dityatev, A., and Fellin, T. (2008) Extracellular matrix in plasticity and epileptogenesis, Neuron Glia Biol., 4, 235–247.
Novak, U., and Kaye, A. H. (2000) Extracellular matrix and the brain: components and function, J. Clin. Neurosci., 7, 280–290.
Dansie, L. E., and Ethell, I. M. (2011) Casting a net on dendritic spines: the extracellular matrix and its receptors, Dev. Neurobiol., 71, 956–981.
Mataga, N., Mizuguchi, Y., and Hensch, T. K. (2004) Experience-dependent pruning of dendritic spines in visual cortex by tissue plasminogen activator, Neuron, 44, 1031–1041.
Wintergerst, E. S., Faissner, A., and Celio, M. R. (1996) The proteoglycan DSD-1-PG occurs in perineuronal nets around parvalbumin-immunoreactive interneurons of the rat cerebral cortex, Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 14, 249–255.
Wang, D., and Fawcett, J. (2012) The perineuronal net and the control of CNS plasticity, Cell Tissue Res., 349, 147–160.
Pyka, M., Wetzel, C., Aguado, A., Geissler, M., Hatt, H., and Faissner, A. (2011) Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans regulate astrocyte-dependent synaptogenesis and modulate synaptic activity in primary embryonic hippocampal neurons, Eur. J. Neurosci., 33, 2187–2202.
Bradbury, E. J., Moon, L. D., Popat, R. J., King, V. R., Bennett, G. S., Patel, P. N., Fawcett, J. W., and McMahon, S. B. (2002) Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury, Nature, 416, 636–640.
Hensch, T. K. (2005) Critical period plasticity in local cortical circuits, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 6, 877–888.
Carulli, D., Pizzorusso, T., Kwok, J. C., Putignano, E., Poli, A., Forostyak, S., Andrews, M. R., Deepa, S. S., Glant, T. T., and Fawcett, J. W. (2010) Animals lacking link protein have attenuated perineuronal nets and persistent plasticity, Brain, 133, 2331–2347.
Gogolla, N., Caroni, P., Luthi, A., and Herry, C. (2009) Perineuronal nets protect fear memories from erasure, Science, 325, 1258–1261.
Suzuki, F., Makiura, Y., Guilhem, D., Sorensen, J. C., and Onteniente, B. (1997) Correlated axonal sprouting and dendritic spine formation during kainate-induced neuronal morphogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice, Exp. Neurol., 145, 203–213.
McRae, P. A., and Porter, B. E. (2012) The perineuronal net component of the extracellular matrix in plasticity and epilepsy, Neurochem. Int., 61, 963–972.
Garwood, J., Rigato, F., Heck, N., and Faissner, A. (2001) Tenascin glycoproteins and the complementary ligand DSD-1-PG/phosphacan-structuring the neural extracellular matrix during development and repair, Restor. Neurol. Neurosci., 19, 51–64.
Faissner, A., Heck, N., Dobbertin, A., and Garwood, J. (2006) DSD-1-proteoglycan/phosphacan and receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase-beta isoforms during development and regeneration of neural tissues, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 557, 25–53.
Okamoto, M., Sakiyama, J., Mori, S., Kurazono, S., Usui, S., Hasegawa, M., and Oohira, A. (2003) Kainic acidinduced convulsions cause prolonged changes in the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans neurocan and phosphacan in the limbic structures, Exp. Neurol., 184, 179–195.
Heck, N., Garwood, J., Loeffler, J. P., Larmet, Y., and Faissner, A. (2004) Differential upregulation of extracellular matrix molecules associated with the appearance of granule cell dispersion and mossy fiber sprouting during epileptogenesis in a murine model of temporal lobe epilepsy, Neuroscience, 129, 309–324.
Kurazono, S., Okamoto, M., Sakiyama, J., Mori, S., Nakata, Y., Fukuoka, J., Amano, S., Oohira, A., and Matsui, H. (2001) Expression of brain specific chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, neurocan and phosphacan, in the developing and adult hippocampus of Ihara’s epileptic rats, Brain Res., 898, 36–48.
McRae, P. A., Baranov, E., Rogers, S. L., and Porter, B. E. (2012) Persistent decrease in multiple components of the perineuronal net following status epilepticus, Eur. J. Neurosci., 36, 3471–3482.
Rankin-Gee, E. K., McRae, P. A., Baranov, E., Rogers, S., Wandrey, L., and Porter, B. E. (2015) Perineuronal net degradation in epilepsy, Epilepsia, 56, 1124–1133.
Yuan, W., Matthews, R. T., Sandy, J. D., and Gottschall, P. E. (2002) Association between protease-specific proteolytic cleavage of brevican and synaptic loss in the dentate gyrus of kainate-treated rats, Neuroscience, 114, 1091–1101.
Yepes, M., Sandkvist, M., Coleman, T. A., Moore, E., Wu, J. Y., Mitola, D., Bugge, T. H., and Lawrence, D. A. (2002) Regulation of seizure spreading by neuroserpin and tissuetype plasminogen activator is plasminogen-independent, J. Clin. Invest., 109, 1571–1578.
Achuta, V. S., Rezov, V., Uutela, M., Louhivuori, V., Louhivuori, L., and Castren, M. L. (2014) Tissue plasminogen activator contributes to alterations of neuronal migration and activity-dependent responses in fragile X mice, J. Neurosci., 34, 1916–1923.
Kurshan, P. T., Phan, A. Q., Wang, G. J., Crane, M. M., Lu, H., and Shen, K. (2014) Regulation of synaptic extracellular matrix composition is critical for proper synapse morphology, J. Neurosci., 34, 12678–12689.
Takacs, E., Nyilas, R., Szepesi, Z., Baracskay, P., Karlsen, B., Rosvold, T., Bjorkum, A. A., Czurko, A., Kovacs, Z., Kekesi, A. K., and Juhasz, G. (2010) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity increased by two different types of epileptic seizures that do not induce neuronal death: a possible role in homeostatic synaptic plasticity, Neurochem. Int., 56, 799–809.
Pitkanen, A., Ndode-Ekane, X. E., Lukasiuk, K., Wilczynski, G. M., Dityatev, A., Walker, M. C., Chabrol, E., Dedeurwaerdere, S., Vazquez, N., and Powell, E. M. (2014) Neural ECM and epilepsy, Prog. Brain Res., 214, 229–262.
Iyer, A. M., Zurolo, E., Boer, K., Baayen, J. C., Giangaspero, F., Arcella, A., Di Gennaro, G. C., Esposito, V., Spliet, W. G., Van Rijen, P. C., Troost, D., Gorter, J. A., and Aronica, E. (2010) Tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase plasminogen activator in human epileptogenic pathologies, Neuroscience, 167, 929–945.
Lahtinen, L., Huusko, N., Myohanen, H., Lehtivarjo, A. K., Pellinen, R., Turunen, M. P., Yla-Herttuala, S., Pirinen, E., and Pitkanen, A. (2009) Expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor is increased during epileptogenesis in the rat hippocampus, Neuroscience, 163, 316–328.
Kopjas, N. N., Jones, R. T., Bany, B., and Patrylo, P. R. (2006) Reeler mutant mice exhibit seizures during recovery from isoflurane-induced anesthesia, Epilepsy Res., 69, 87–91.
Slaker, M., Chuchill, L., Todd, R. P., Blacktop, J. M., Zuloaga, D. G., Raber, J., Darling, R. A., Brown, T. E., and Sorg, B. A. (2015) Removal of perineuronal nets in the medial prefrontal cortex impairs the acquisition and reconsolidation of a cocaine-induced conditioned place preference memory, J. Neurosci., 35, 4190–4202.
Geissler, M., Gottschling, C., Aguado, A., Rauch, U., Wetzel, C. H., Hatt, H., and Faissner, A. (2013) Primary hippocampal neurons, which lack four crucial extracellular matrix molecules, display abnormalities of synaptic structure and function and severe deficits in perineuronal net formation, J. Neurosci., 33, 7742–7755.
Schousboe, A., Madsen, K. K., Barker-Haliski, M. L., and White, H. S. (2014) The GABA synapse as a target for antiepileptic drugs: a historical overview focused on GABA transporters, Neurochem. Res., 39, 1980–1987.
Fries, P., Nikolic, D., and Singer, W. (2007) The gamma cycle, Trends Neurosci., 30, 309–316.
Ma, Y., and Prince, D. A. (2012) Functional alterations in GABAergic fast-spiking interneurons in chronically injured epileptogenic neocortex, Neurobiol. Dis., 47, 102–113.
Sessolo, M., Marcon, I., Bovetti, S., Losi, G., Cammarota, M., Ratto, G. M., Fellin, T., and Carmignoto, G. (2015) Parvalbumin-positive inhibitory interneurons oppose propagation but favor generation of focal epileptiform activity, J. Neurosci., 35, 9544–9557.
Shiri, Z., Manseau, F., Levesque, M., Williams, S., and Avoli, M. (2015) Interneuron activity leads to initiation of low-voltage fast-onset seizures, Ann. Neurol., 77, 541–546.
Saghatelyan, A. K., Nikonenko, A. G., Sun, M., Rolf, B., Putthoff, P., Kutsche, M., Bartsch, U., Dityatev, A., and Schachner, M. (2004) Reduced GABAergic transmission and number of hippocampal perisomatic inhibitory synapses in juvenile mice deficient in the neural cell adhesion molecule L1, Mol. Cell. Neurosci., 26, 191–203.
Hoffmann, K., Sivukhina, E., Potschka, H., Schachner, M., Loscher, W., and Dityatev, A. (2009) Retarded kindling progression in mice deficient in the extracellular matrix glycoprotein tenascin-R, Epilepsia, 50, 859–869.
Kim, S. Y., Porter, B. E., Friedman, A., and Kaufer, D. (2016) A potential role for glia-derived extracellular matrix remodeling in postinjury epilepsy, J. Neurosci. Res., 94, 794–803.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L. G. Khaspekov, L. E. Frumkina, 2017, published in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 3, pp. 528-541.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khaspekov, L.G., Frumkina, L.E. Molecular mechanisms mediating involvement of glial cells in brain plastic remodeling in epilepsy. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 380–391 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917030178
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917030178